
Geography of Beijing
Beijing -- the Capital of the People's Republic of China with the excellent geography. Located at the northern tip of the North China Plain, near the meeting point of the Xishan and Yanshan mountain ranges. The city is 150 km inland from the Bohai Sea via Tianjin Municipality in the southeast. Aside from Tianjin, Beijing is bordered on all other sides by Hebei Province, including a piece wedged between Beijing and Tianjin. Due it its strategic location, Beijing is an important international trading center.
Beijing city covers a total area of 16,807.8 sq. km. The terrain is roughly 38% flat and 62% mountainous. The Great Wall of China was built across the mountains north of Beijing to guard against nomadic invasions. The city itself lies on flat land that opens to the east and south. The much larger Beijing Municipality encompasses mountains that surround the city from the southwest to the northeast and reach elevations of over 2,000 m.
Beijing's Administrative Divisions
Beijing Municipality consists of eight city districts, eight suburban districts and two rural counties. In imperial times, the old walled city of Beijing occupied 62 sq. km. The physical size of the city has grown more than tenfold in recent decades to about 750 sq. km.
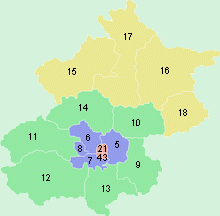
Four districts, Dongcheng [1], Xicheng [2], Chongwen [3] and Xuanwu [4] form the urban core of Beijing. They occupy the area inside the old walled city, Today, Line 2 loop of the Beijing Subway traces the inner city wall, The Tiananmen Square and Forbidden City, where the center of the city, both belong to Dongcheng.
Beyond the 2nd Ring Road, the city spreads out in a checkerboard fashion marked by concentric ring roads. Chaoyang [5], Haidian [6], Fengtai [7] and Shijingshan [8], were once considered on the city¡¯s outskirts, but are now integral parts of the city inside the 5th Ring Road.
Of the suburban districts further afield, Tongzhou [9] and Shunyi [10] in the east are rapidly urbanizing. Mentougou [11] and Fangshan [12] lie to the west, Daxing [13] District to the south, and the famous tourist district -- Changping [14] just north of the city ranges from densely urbanized Tiantongyuan in the south to the Juyongguan Great Wall in the north. In between are the Thirteen Ming Tombs and the Eastern Qing Tombs.
Far north of the municipality in the Yanshan range are Yanqing [15] and Miyun [16] Counties, and Huairou [17] and Pinggu [18] Districts, both of which were rural counties until 2001. The far north is rugged, rural and sparsely populated. Yanqing, Huairou and Miyun all have fewer than 200 residents per sq. km. They are perhaps best known for stretches of the Great Wall, with Badaling and Shuiguan in Yanqing, Mutianyu, Huanghuacheng and Jiankou in Huairou, and Gubeikou and Simatai in Miyun, and Jiangjunguan in Pinggu.
Beijing's Climate
Four distinct seasons are a major highlighting feature of the Geography of Beijing, characterised by hot, humid summers due to the East Asian monsoon, and generally cold, windy, dry winters that reflect the influence of the vast Siberian anticyclone. Average Temperatures of Beijing in January are at around 1 ¡ãC, while average temperatures in July are around 30¡ãC. The highest temperature ever recorded was 42 ¡ãC and the lowest recorded was -27 ¡ãC. With late spring and autumn being the best seasons for tourists to visit the city, Autumn is regarded as the golden tourist season of the year.
Beijing-travels.com offers online information on Beijing Geography and More introduction of Beijing, Keep browsing our site for more information on Beijing China.
Special Offer Travels
Beijing-Travels.com is a full service local travel agency offers popular travel packages to Beijing, Great Wall and all over of China. We specialize in "PRIVATE" & "NO-SHOPPING" tours and try to be original, unique and best to satisfy our clients, Let us assist you to experience your own vacations!

